Blog
Experience the excellence of our solutions in the Internet of Things (IoT), Software Development, and Mobile App Development. Our services are designed to accelerate your project's success and bring your ideas to life.
What are core web vitals? Why is it essential for every website, and how to improve them?
SEO ranking factors, core web vitals, google algorithm, Google updates, SEO marketing, website ranking strategies, largest contentful paint, first input delay, cumulative layout shift
Imagine a scenario:
So, you have hired an SEO company and dedicated a big budget for SEO.
You have started working on various SEO activities such as on-page optimization, content marketing, guest posting, off-page activities, etc.
Six months passed, and you are still not getting good, genuine leads for your website. However, your sales and revenues before you hired the agency were good compared to the last six months.
What should you do? You are in a dilemma. The agency guys ask you to have some patience as SEO is a long-term process, and it takes some time to get desired outcomes.
The solution is simple. You need to learn something about SEO, SEO ranking factors, how Google works, and much more. Then, when you have some information about SEO, you will know what the agency guys are doing.
We all know how search engine optimization works.SEO marketing professionals perform many activities to improve your website’s authority and awareness to get you on the top position of Google when someone searches for relevant keywords.
This blog will help you understand some key web vitals that play an essential role in your brand’s SEO strategy. After reading the post, you will know many things about SEO. If you are lucky, you might also know what is the issue why your website is not there on Google’s first page.
What are core web vitals?
Everyone related to the SEO industry is talking about core web vitals. When your core web vitals are great, you will see improved rankings for keywords.
Also, core web vitals improve the experience of a user when he visits a particular page. Google recently stated that it would consider page experience as one of the ranking factors.
Most of the time, when you stay tuned with the latest Google updates, you will be able to understand what Google wants. Therefore, you need to know the latest Google updates to incorporate details in your SEO strategy.
There are three core web vitals your website has to be good at to rank higher on Google search engine page results.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
- First Input Delay (FID)
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
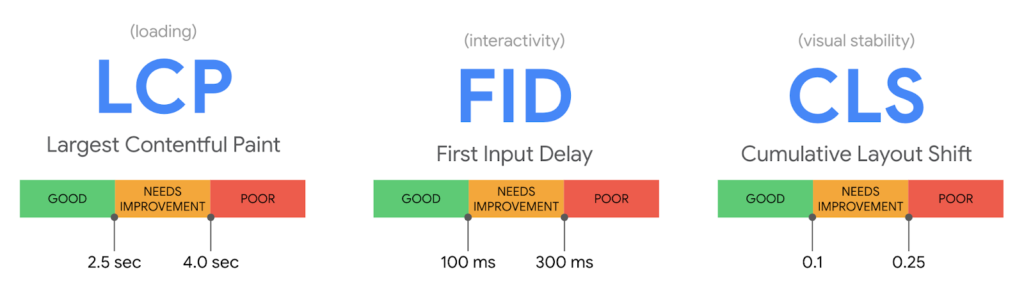
Image Source: searchenginejournal.com Image Source: searchenginejournal.com
You can check out how your website’s core web vitals are performing on the Google Search Console. If one or more core web vitals are not performing well, you need to improve them.
Before we discuss more core web vitals, it is important to learn what field data and lab data are:
1. Field Data
SEO professionals get field data from real users who visit your website. It is gathered through the CRUX (Chrome User Experience Report)report.
2. Lab Data
SEO professionals get lab data without any involvement from any real users. Lab data is gathered within a controlled environment.
When Google measures user experience for a particular page, it checks three parameters:
- Whether a website is mobile-friendly or not.
- Whether a website offers HTTPS (secure experience)
- Whether a website is free of intrusive interstitials.
You can check more about Google update sabout page experience here.
This guide will help you to get correct and factual information about core web vitals. This is your best resource to know about core web vitals. In addition, as the Google algorithm changes its priorities from time to time, you need to stay updated with Google updates.
People say that core web vitals are all about how fast your website pages load. It is not true. Core web vitals are much more than just speed.
Core web vitals give you exact information about your website’s page experience by offering a set of metrics related to speed, responsiveness, and visual stability.
Why are core web vitals important?
There are three main reasons to care for core web vitals.
- When you visit a website, the first thing that you will expect is speed. You don’t want the website you visit to take more time to load. Another thing is the visual appeal and responsiveness of the website on any device. The core thing is user experience plays a huge role when you want visitors to take action on your website.
- Google has already declared that core web vitals are important. Until you get any new updates, you have to improve your core web vitals to rank higher on Google search engine results.
- When you pass the core web vitals assessment, you will offer a good user experience to your visitors. Google will come to know that your website is showing the correct information to visitors, and it will make a note of it.
So when your visitors are happy, you will notice more conversions and revenues. It is as simple as that. A few case studies can show how page loading differences of even milliseconds can affect bounce rates and conversions.
Now, let’s talk about each of these web vitals metrics.
1. LARGEST CONTENTFUL PAINT (LCP)
Largest Contentful Paint is a metric that measures the actual time of your page’s loading. It starts when your page starts loading to when the last image or text renders on the screen.
What is the aim here? The main objective of LCP is to measure the loading time of the main contents of the page. You can check out your page’s LCP in-field data and lab data.
The browser stops reporting new LCP candidates in the field as soon as the user takes some actions like clicking on text or image, switching tabs, or closing the tab.
In the lab, there is no clear indication as to when the LCP is finished.
When you are measuring LCP, there is a chance that the largest text or image block may change. In such a case, the most recent candidate is considered.
Determining your LCP candidates for each page is very crucial. First, you need to list down the most eligible LCP candidates for each page. The most eligible LCP candidate might be the H1 or the cover image of a blog post. For product pages, it might be the product image.
Now that you have a list ensure that these particular LCP candidates are displayed on the page as soon as possible.
If your LCP score is less than 2.5 seconds, it is considered a good score. If it is between 2.5 to 4 seconds, you need some improvements. If it is more than 4 seconds, it is poor.
The reasons for a poor LCP score
It might be anything from slow server response time, too heavy content resources, and many more. First, check out your server response time to know whether you have any infrastructure issues or not. Then, you can upgrade your hosting platform. Also, check out your firewall or DNS setting.
How to improve your LCP score?
You can perform various things to improve your LCP score. Some things you can do are:
- Optimize the critical rendering path.
- Optimize your website’s CSS and images.
- Remove unnecessary third-party scripts that are not needed.
- Upgrade your host if you are having hosting issues.
- Enabling lazy loading also helps to improve your LCP score.
2. FIRST INPUT DELAY (FID)
As they say, the first impression is the last; you need to ensure that you lure your visitor in the first place to make them take action.
First Input Delay is a core web vital that is highly crucial. It measures the actual amount of time in milliseconds from the moment a user interacts with the website to the moment a browser responds to the interaction.
A user’s interaction might be clicking on the link, tapping on a button, or pressing a key.
The FID can be measured in the field only and not in the lab. It is all about how successfully you lure your visitor in the first place. Ensure that your website’s FID is lower.
If you want to measure FID in the lab, you can use the Total Blocking Time metric close to First Input Delay.
Remember that users’ actions such as scrolling or zooming are not considered actions as they have different performance constraints. For example, the scrolling is performed by the GPU and not the CPU.
If your FID score is less than 100 milliseconds, it is considered good. If it ranges between 100 to 300 milliseconds, improvements are needed. The FID score of more than 300 milliseconds is considered poor.
Reasons for a low or poor FID score
Experts believe that the main potential reason for a poor FDI score is the browser’s main thread executing JavaScript code. If it is the case, it might not respond quickly to users’ interactions.
How to improve your FID score?
- Try to reduce your website’s JavaScript execution time
- Ensure that you minimize the work in the main thread.
- Remove any unnecessary third-party scripts.
- Use a browser cache to display your page contents faster.
3. CUMULATIVE LAYOUT SHIFT (CLS)
The main aim of Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) is to check out the visual stability.
Imagine when someone clicks on your website page, and all text, images, videos, and other elements behave crazy. It is not visual stability. Instead, it will give you a high CLS, and it isn’t nice.
Visual stability is crucial to offer a pleasant experience to visitors. You can check out CLS in both field data and lab data. Ensure that your CLS score is low.
One thing to remember here is that CLS is not measured in seconds. Here, it checks out elements that can move between two frames. It measures the movement in the viewport. When the visitor clicks on some link or fills a field, visual instability might lead to misclicking. For a user, it might turn into a negative experience.
You might end up getting two different scores on field data and lab data as tools used to gather lab data take notes for a very short period.
If your CLS score is less than 0.1, it is good. e If it is between 0.1 to 0.25, you need improvements. If it is greater than 0.25, it is considered poor.
Reasons for a poor CLS score
It might be images or ads without defined dimensions, dynamically injected elements, web fonts causing a flash of invisible text, or newly added DOM elements above content that have been loaded.
How to Improve your CLS Score?
- Ensure that all media, including images, ads, videos, and GIFs, have specified dimensions.
- Also, ensure that all ads have reserved spaces.
- Ensure new user interface elements are below the fold.
- Use system fonts rather than web fonts.
WRAPPING UP
That is all. These are core web vital that you need to know. Therefore, it is vital to work on these web vitals and pass the core web vitals assessment.
Also, it is not a one-time job. You need to measure these core web vitals from time to time. If you find any abnormalities in any of these core web vitals, take action.
Core web vitals are the determining factors of your website’s ranking on Google. Therefore, you must understand the importance and start improving them.


.png&w=640&q=75)
